Nature's Unifying Patterns
Detailed descriptions and examplesNature runs on information.
To be attuned to their environment, organisms and ecosystems need to receive information from the environment and be able to act appropriately in response to that information. This includes sending and receiving signals to and from other organisms or even within the body of an organism. This system of send, receive, and respond has been finely tuned through millions of years of evolution. Some living systems work within narrow ranges of optimal conditions, so they need to constantly monitor their environment and respond. Others have broader ranges, but still need to be able to detect and respond when conditions are such that they approach their limits (e.g., maximum survivable temperature or oxygen availability). Using feedback loops is one way to monitor those conditions. Both negative feedback loops (those that slow down a process), and positive feedback loops (those that speed up a process) are important in natural systems.
Biology Examples
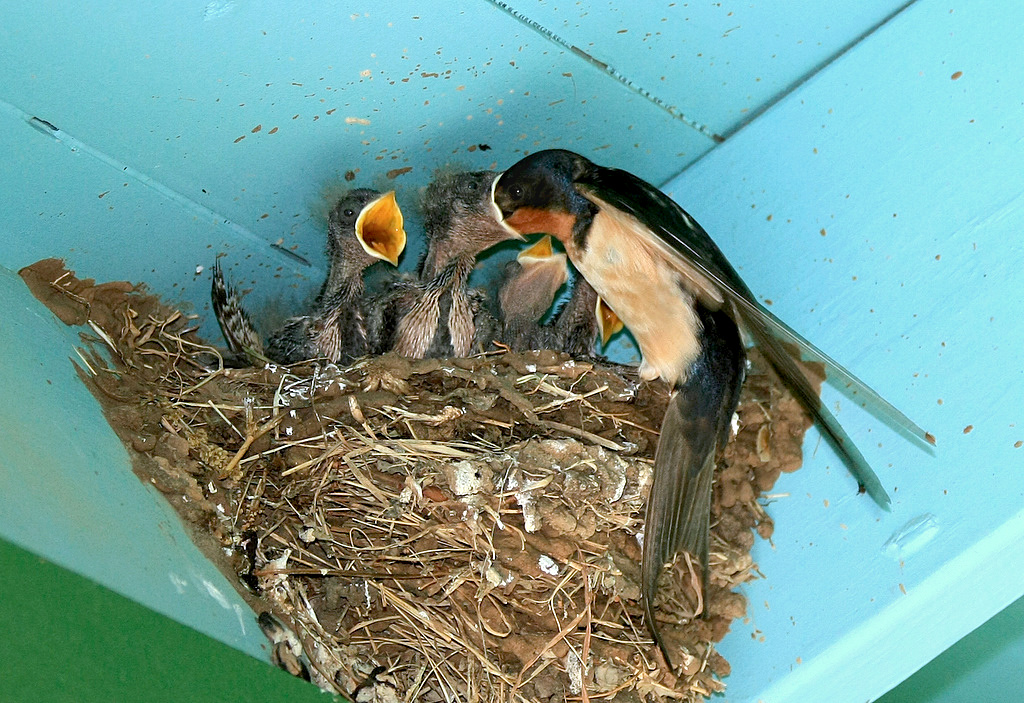
Songbirds

Acacia tree
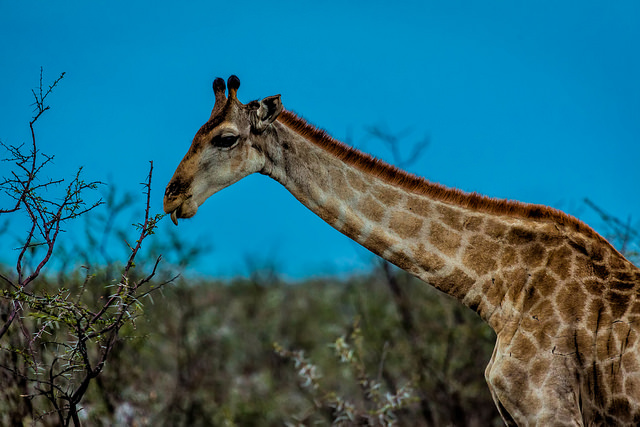

Giraffe browsing on an acacia tree.
Design Applications
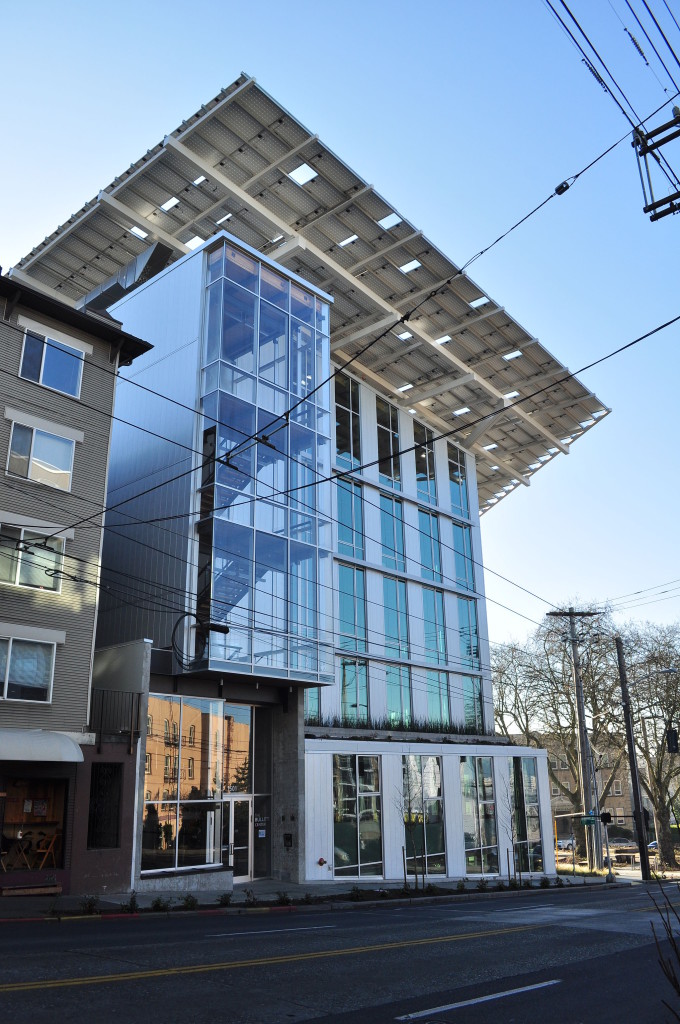
Bullitt Center

Nike Fuel Band

Pandora

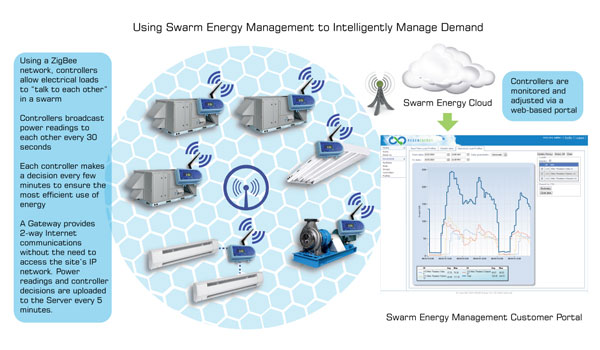
Regen Energy
Image Credits
Baby birds: Ken Slade, CC-BY-NC
Acacia and giraffe: Baron Reznik CC-BY-NC-SA
Bullitt Center: Joe Mabel CC-BY-SA via Wikimedia
Nike Fuel Band: Peter Parkes CC-BY
Regen Energy: via Regen company website